In the world of fitness and bodybuilding, a lot of information circulates about gaining muscle mass. However, not everything you hear is true. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore some of the most common myths associated with gaining muscle mass and separate the truth from the myth. Understanding these misconceptions can help you plan your training and diet more effectively, ensuring solid, lasting results.
Myth 1: “You need large amounts of protein to gain muscle mass.”
We often hear the recommendation that to gain muscle mass, it is necessary to consume large amounts of protein. While protein is indeed essential for building muscle, consuming excessive amounts will not necessarily result in more gains. The truth is that the quality and proper distribution of protein throughout the day are more important than the total quantity.
Studies show that the body can only utilize a certain amount of protein per meal for muscle synthesis, usually around 20-30 grams. Consuming more than this in a single meal may not provide additional muscle-building benefits. Instead, it’s important to spread your protein intake throughout the day and include high-quality protein sources, such as lean meats, eggs, dairy, and legumes, at each meal.
Myth 2: “Cardio hinders muscle mass gain.”
A common myth is that doing cardiovascular exercise, such as running or cycling, can harm muscle mass gain. However, this is not necessarily true. While cardiovascular training can increase calorie expenditure and potentially interfere with muscle recovery if done excessively, incorporating cardio in moderation can even be beneficial for gaining muscle mass.
Studies show that cardiovascular training can improve cardiovascular fitness and help with fat loss, which can reveal the muscles you’re building with strength training. Additionally, cardio can aid recovery by increasing blood flow to the muscles, which can speed the removal of metabolites and promote muscle regeneration.
Myth 3: “Women shouldn’t lift heavy weights.”
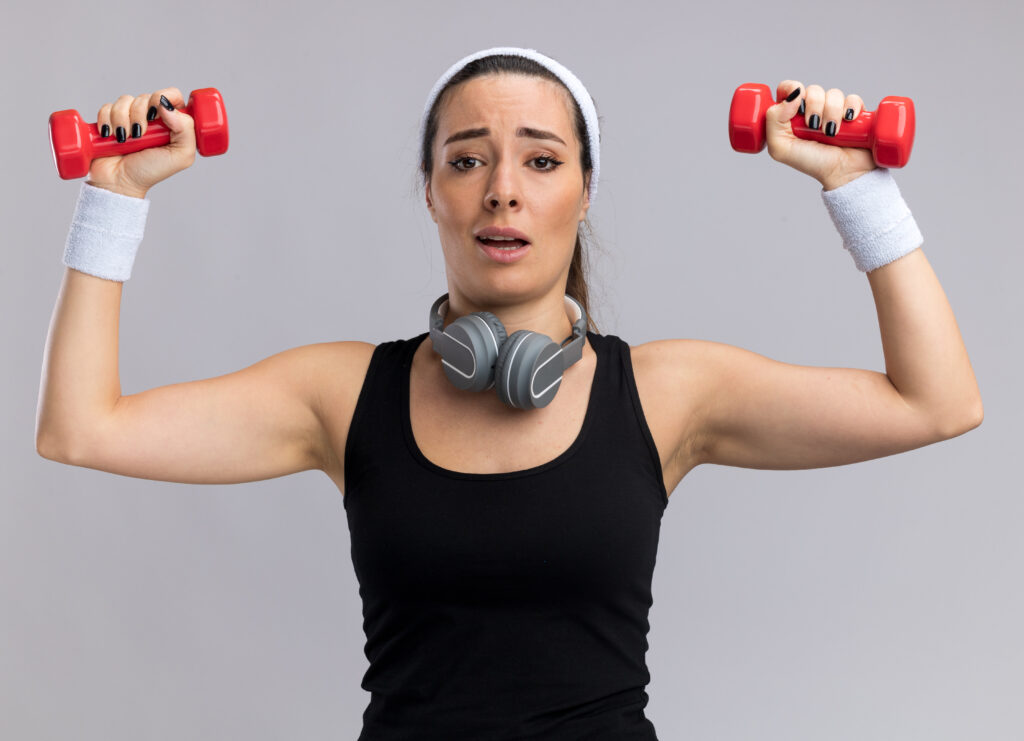

A persistent misconception is that lifting heavy weights is inappropriate or harmful for women, resulting in a bulky, masculine body. In reality, heavy strength training is extremely beneficial for women and can help achieve a variety of fitness and aesthetic goals.
Women do not have the same amount of testosterone as men, which means they are very unlikely to develop excessively large and bulky muscles just by lifting weights. Instead, strength training can help women tone and define their bodies, increase strength and endurance, improve bone health, and promote fat loss.
Myth 4: “You can only gain muscle mass if you take supplements.”
A common misconception is that supplementation is essential for gaining muscle mass. Although supplements can be useful to complement a balanced diet, they are not necessary for gaining muscle mass. In fact, most nutritional needs can be met through a varied and balanced diet.
Protein powder, for example, may be convenient for those who have difficulty meeting their daily protein goals through whole foods, but it is still possible to get enough protein from natural food sources such as meat, fish, eggs and dairy. Likewise, other supplements, such as creatine and BCAAs, may offer additional benefits, but are not essential for successful muscle gain.
Myth 5: “You need to train every day to gain muscle mass quickly.”
A common myth is that you need to train every day to gain muscle mass quickly. However, this can lead to overtraining and even harm your long-term results. The truth is, rest and recovery are just as important as the training itself when it comes to building muscle.
During strength training, muscles suffer minor injuries that need time to repair and grow. It is during the rest period that muscle synthesis and real gains in muscle mass occur. Therefore, it’s important to give your body time to recover between workouts and ensure you’re getting adequate sleep, adequate nutrition, and proper stress management.
Myth 6: “Gaining muscle mass is just a matter of genetics.”
A common myth is that muscle mass gain is determined solely by genetics and that some people simply do not have the ability to build muscle. Although genetics play an important role in determining an individual’s response to strength training, it is possible for anyone to experience significant muscle gains with proper training and proper nutrition.
Studies show that most people can gain about 1-2 pounds of muscle per month with consistent training and a proper diet. The key is to follow a well-structured training program, focus on gradual progression, and stay consistent over the long term. With dedicated time and effort, it is possible to transform your body and achieve the results you want, regardless of your genetics.
Myth 7: “You can turn fat into muscle.”
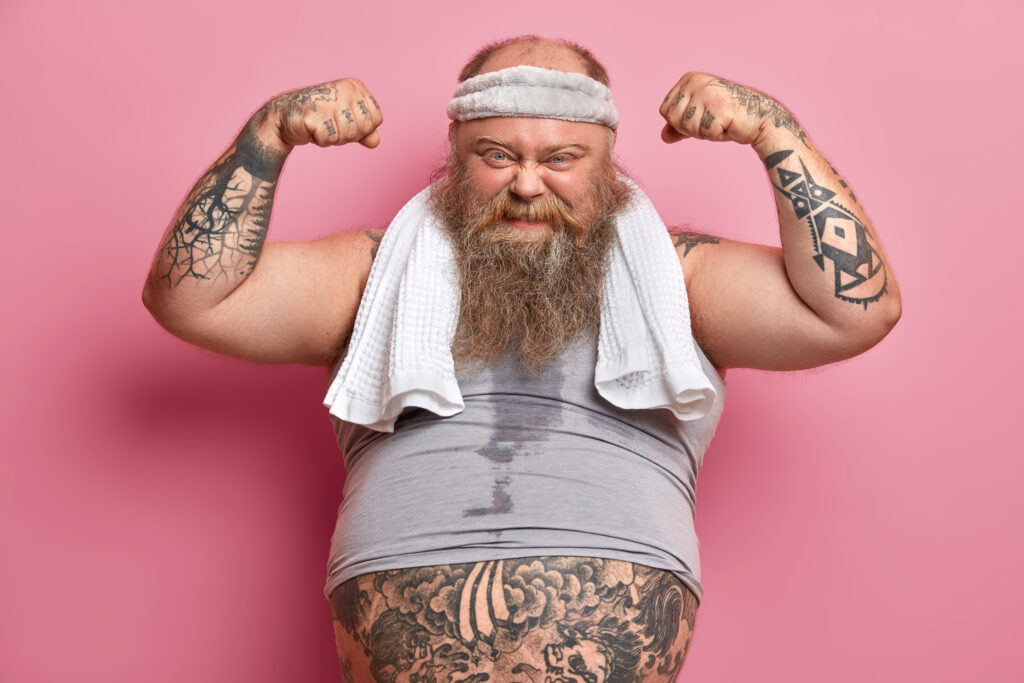

A common myth is that it is possible to turn fat into muscle and vice versa. However, this is not true. Fat and muscle are different tissues and cannot be directly converted into one another. Instead, it’s possible to lose fat and gain muscle simultaneously through a combination of strength training, cardio, and proper nutrition.
When you follow a strength training program and a balanced diet, your body burns fat for energy and uses nutrients to repair and build muscle. As a result, you may experience a decrease in body fat and an increase in lean muscle mass. However, this requires a controlled calorie deficit combined with proper training and nutrition.
Myth 8: “Gaining muscle mass is only for young people.”
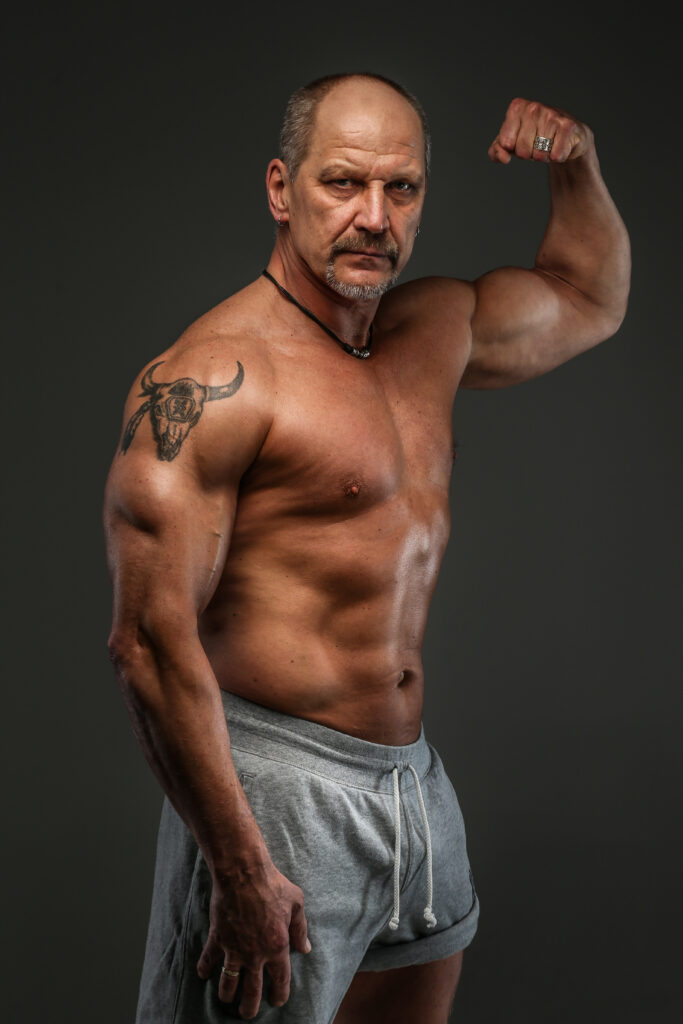

A common misconception is that gaining muscle mass is exclusive to young people and that it is impossible for older people to build muscle. In reality, people of all ages can experience significant muscle gains with proper training and proper nutrition.
Studies show that even older people can experience muscle hypertrophy and significant strength gains with regular strength training. In fact, strength training can be particularly beneficial for older adults, helping to prevent age-related muscle loss, improve physical function, and promote bone health.
Conclusion:
By separating myths from reality, it is possible to adopt a more effective and realistic approach to gaining muscle mass. By understanding that there are no shortcuts or quick fixes and that success requires hard work, dedication and patience, you will be on the right path to achieving your fitness goals. Always remember to seek evidence-based knowledge, listen to your body, and follow a training and diet plan that is sustainable over the long term.
References:
- Phillips, S. M., & Van Loon, L. J. (2011). Dietary protein for athletes: from requirements to optimum adaptation. Journal of Sports Sciences, 29(sup1), S29-S38.
- Kraemer, W. J., & Ratamess, N. A. (2004). Fundamentals of resistance training: progression and exercise prescription. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 36(4), 674-688.
- Westcott, W. L. (2012). Resistance training is medicine: effects of strength training on health. Current Sports Medicine Reports, 11(4), 209-216.
- Campbell, B., Kreider, R. B., Ziegenfuss, T., La Bounty, P., Roberts, M., Burke, D., … & Antonio, J. (2007). International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: protein and exercise. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 4(1), 8.